- Understand the dual blood supply of the liver and how it distributed and interacts with liver cells.
- Define the concept of the classic liver lobule and recognize it in histological liver sections.
- Learn about the structure of portal triads and identify its components.
- Understand the structure of hepatic cords and liver sinusoids.
- Learn about and identify the cells of the liver tissue: Hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, and endothelial cells. Know about hepatic stellate/Ito cells and their functional and pathological relevance.
- Discuss the ultrastructural features and functional aspects of hepatocytes.
- Understand the concept of the acinus of Rappaport and how it is important for understanding liver pathology.
- Discuss and recognize the production of bile and the cellular structures involved.
- Study the histological features of the gallbladder and be able to identify it.
Slide 001 Liver (monkey) H&E View Virtual Slide
Task:
- Overview of liver organization
Using the low power objective observe numerous small, pale spots in the parenchyma, most of which are either central veins or small branches of portal veins (in portal canals). There may be a few larger channels, which are larger veins either entering or leaving this region of the liver. Try to identify classic liver lobules vs. portal lobules vs. acini of Rappaport.
Slide 194 Liver, gall bladder H&E View Virtual Slide
Slide 198 Liver, silver stain showing the collagen III reticular fibers in the space of Disse View Virtual Slide
Tasks:
- Identify central veins and portal triads; identify components of portal triads (the links below show these in slide 001, but you should try to find them on your own in slide 194)
- Follow the flow of blood between hepatic cords
- Identify Kupffer cells
- Look for the endothelial lining of the liver sinusoids
The central veins slide 001 central veins, terminal hepatic venules View Image (also referred to as terminal hepatic venules) are surrounded intimately by hepatocytes similar to those that make up the bulk of the liver tissue. Portal veins slide 001 portal vein View Image at medium power appear in section as a circle of rather prominent nuclei. In small branches of the hepatic artery slide 001 hepatic artery View Image you will see primarily the ring of smooth muscle that makes up their wall. The three components together (portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct) constitute a portal triad. Look for good examples of portal canals where all three components are seen well. Keep in mind that these structures twist and turn so there may be more than one cross section of a bile duct, artery, or vein, so it's not always a "triad" of structures that you'll see in the portal canal. Now, see if you can define a classic liver lobule at low power.
In the hepatic parenchymal tissue, note the plates of hepatocytes (the arrangement of these cells in plates is not always clear, due to plane of section and the frequent interconnections of plates). Occasional hepatocytes are binucleate. Between the plates of hepatocytes are intervening sinusoids lined by a thin endothelium. Larger eosinophilic cells lining the sinusoids are mostly Kupffer cells slide 194 Kupffer cells View Image (a type of macrophage, part of the mononuclear phagocyte system). Look for Kupffer cells using slide 194 as these cells are not readily recognized in slide 001. You should be able to distinguish Kupffer cells from endothelial lining cells.
The space between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes is called the “space of Disse” and is somewhat artificially enlarged in conventional sections. The reticular fibers in this space of Disse are visualized in silver-stained slide 198. Remember that blood flows from the portal veins and hepatic arteries (of the portal canals) through the sinusoids to the central veins. A classical liver lobule has a central vein in its center and has several portal triads at its periphery. Bile flows through the bile canaliculi (too small to see) to the canals of Hering to bile ducts in portal canals, to hepatic ducts of increasing sizes and to the common hepatic duct, eventually to be emptied into the duodenum via the common bile duct. If you really want to find a canal of Hering, look for a line of low cuboidal cells slide 001 canal of Hering View Image immediately adjacent to a portal canal --the canal of Hering connects canaliculi to the bile duct.
This portal inflow system can be distinguished from the portal outflow system which lacks accompanying arteries and bile ducts. The hepatic outflow system starts with central veins which empty into sublobular veins and into collecting veins of various sizes and eventually into the hepatic veins (remember from Gross Anatomy the 3 large veins that empty into the inferior vena cava!). One characteristic of the hepatic outflow system is that it cuts through the liver parenchyma without respecting the organization of the liver lobules. The portal inflow system, on the other hand, is always located at the periphery of each liver lobule.
Slide 198-1 Liver, bile canaliculi silver stain View Virtual Slide
Task:
- View the organization of bile canaliculi
One of the difficult concepts in the study of this organ is to understand the three-dimensional arrangement of the bile canaliculi. Slide 198-1 is a rather thick section of liver that has been treated with silver salts in a manner that specifically stains these structures. The liver cells are unstained and so are not seen. Try to gain some understanding of the “chicken-wire” arrangement of the canaliculi as they extend between all cells in the plate of hepatocytes, eventually leading to the portal canal, where the bile is delivered to bile ductules and then to bile ducts.
219 Liver - Central Vein Region View Virtual EM Slide
Note that the sinusoids drain into the central vein. Squamous endothelial cells lining the vessel are clearly seen.
220 Liver Parenchyma View Virtual EM Slide
In the Kupffer cell note occasional lysosomes, which are involved in the phagocytic activities of this cell type. The endothelial lining of the sinusoid is discontinuous, allowing free passage of materials into the space of Disse (note the numerous short microvilli extending from the surface of hepatocytes into this space). There is no organized basal lamina along the endothelial cells or hepatocytes.
223 Liver - Small Portal Triad View Virtual EM Slide
Differentiate between the portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct that make up the portal “triad” and note the connective tissue that surrounds them. In the liver tissue around the portal area you will see plates of hepatocytes, with sinusoids between them. Bile canaliculi can be seen as small white spots between hepatocytes. The sinusoids are lined by endothelial cells and contain occasional Kupffer cells
Slide 194 liver, gall bladder H&E View Virtual Slide
Slide 195M liver, gall bladder Masson View Virtual Slide
Upon gross examination of slides 194 and 195M (i.e. with the naked eye or at the lowest power on the virtual microscope) you will see a portion of the gall bladder wall nestled in an indentation of the liver tissue. Examine the wall of the gall bladder with your microscope. Extensive folds of the mucosa extend into the lumen. The mucosa consists of a tall, simple columnar epithelium and its underlying connective tissue (constituting a lamina propria). No submucosa is defined. The muscularis consists of scattered bundles of smooth muscle. Deep to the muscularis is an adventitia consisting of rather dense connective tissue that binds the gall bladder to the liver. Where the surface of the gall bladder faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
224 Gall bladder epithelium Gall Bladder Epithelium (Simple Columnar Epithelium) View Virtual EM Slide
Review the role of the gall bladder epithelium in absorption and concentration of bile.
1. Which of the following statements regarding the three zones comprising the liver acinus (of Rappaport) is CORRECT?
- Zone 1 is closest to the central vein.
- Zone 2 is the first to undergo necrosis if circulation is impaired.
- Zone 3 is closest to branches of the hepatic artery.
- Zone 1 is the first to receive nutrients delivered by the portal vein.
- Zone 2 is the last to receive any toxins that may be in the blood.
Answer
Correct answer 4. Zone 1 is the first zone to receive nutrients, which are supplied by the portal vein and are delivered to the sinusoids by the distributing venules.
2. The organ/region of the GI tract is depicted in the blow micrograph?
View Image
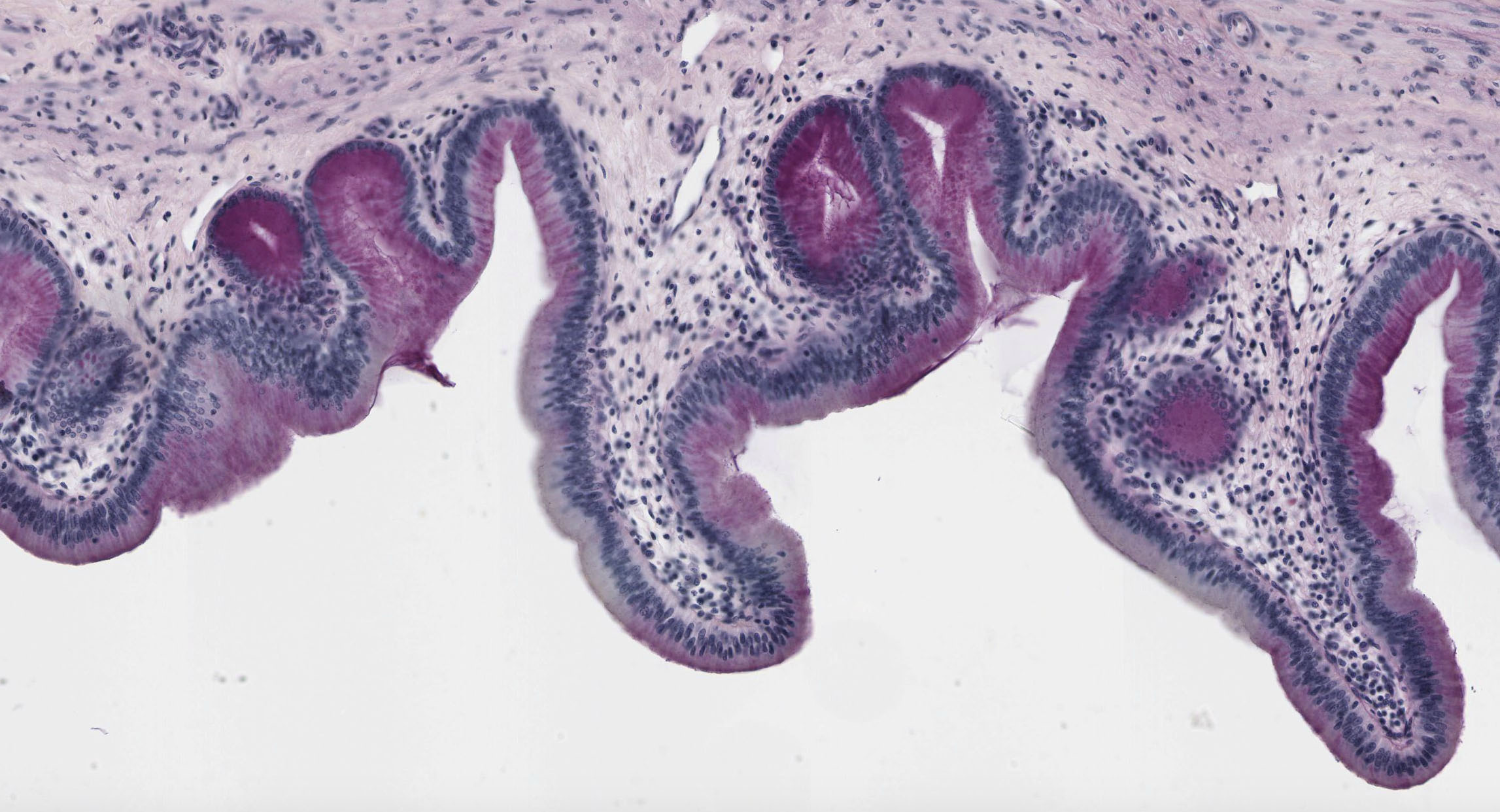
- The lower esophagus
- The cardia of stomach
- The pylorus of stomach
- The duodenum
- The gall bladder
- The jejunum
- The appendix
- The colon
Answer
Correct answer 5., a gall bladder.
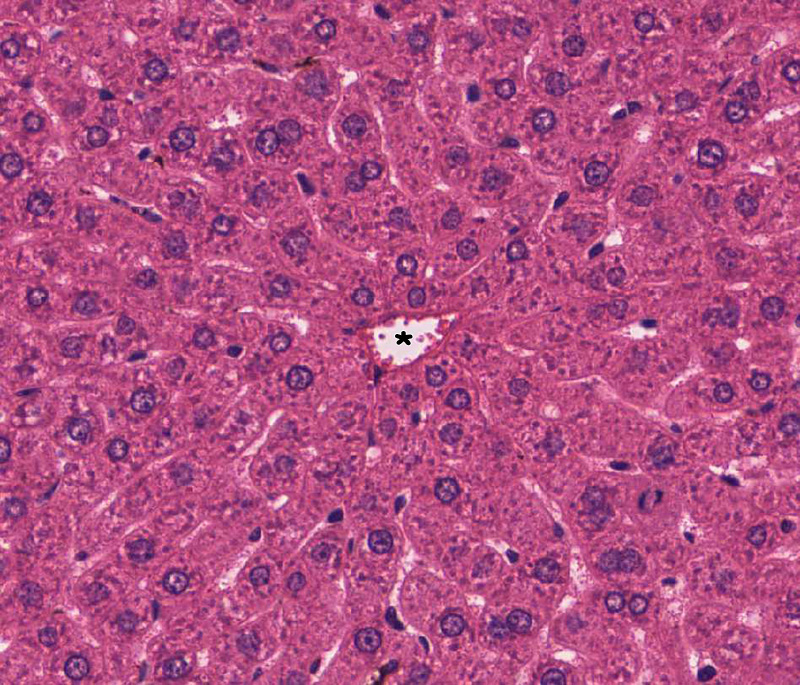
3. Identify the location of the black asterisk.
- A liver sinusoid
- The space of Disse
- A central vein
- A branch of hepatic artery
- A bile duct
- A pancreatic intercalated duct
- A pancreatic interlobular duct
Answer
Correct answer 3. Noting the abundance of hepatocytes, the image is from a liver. The vessel is not part of a portal triad, leaving a central vein as the most likely answer.